| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
| 29 | 30 |
- chord substitution
- walking bass
- minor
- major scale
- tuplet
- 마멘키사우루스
- Augmented
- dominant chord
- 완화치료
- 갈색과부거미
- quadruple meter
- figured bass
- parallel keys
- beams
- 전두측두엽치매
- relative keys
- tonal harmony
- clef
- 역정보
- 워킹 베이스
- time signature
- 심장박동
- tempo
- tonic chord
- lead-sheet symbols
- Inversion
- duple meter
- triple meter
- 대리코드
- copilot
- Today
- Total
트러블해이팅 마인드
대리코드에 대한 이해 본문
음악을 짤짤이로 하고 있다. 그래서 내용이 정확하지 않을 수 있지만 위키나 블로그 글들을 통해 내용을 정리해보려고 한다.

1. 대리코드란?
대리코드를 영미권에서는 chord substitution이라고 표현하는 듯 하다.[1]
In music theory, chord substitution is the technique of using a chord in place of another in a progression of chords or a chord progression. Much of the European classical repertoire and the vast majority of blues, jazz and rock music songs are based on chord progressions. "A chord substitution occurs when a chord is replaced by another that is made to function like the original. Usually substituted chords possess two pitches in common with the triad that they are replacing."

위 그림 1은 C7의 대리코드가 F#7인 것을 설명하고 있는데 두 코드가 공유하는 음은 E와 Bb/A#임을 확인할 수 있다. 도미넌트의 대리코드는 원래의 도미넌트 코드와 증 4도의 관계에 있는 것으로 보인다.

2. 유형
1) ii-V substitution: 어떤 코드 앞에 그 코드의 supertonic (ii7)과 dominant (V7), 혹은 dominant (V7)만 선행하는 경우.
· 예를 들어 C major chord 앞에 Dm7과 G7이 선행하는 경우.
2) Chord quality alteration: 이건 설명을 봐도 잘 모르겠다.
3) Diminished seventh chord
· dominant 7th chord의 대리코드로 사용된다. 예를 들어 A major key에서 E7 (E, G#, B, D)는 G#dim7 (G#, B, D, F)로 대리될 수 있다. 이 예에서, G#dim7 코드 다음으로 I chord인 A가 오게 되면 이러한 진행은 chromatic root movement를 만들게 되어 5도권으로 진행하는 곡에서 변화를 줄 수 있다.
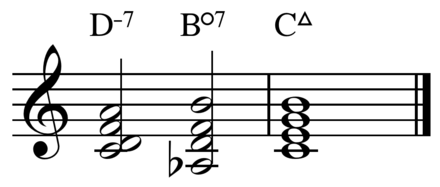
4) Tritone substitution
· 서두에서 잠깐 언급했지만 3음과 7음을 공유하는 코드가 곧 대리코드가 된다. 예를 들어, G7 (G, B, D, F)의 tritone substitution은 Db7 (Db, F, Ab, Cb)가 된다.
· 이 방법은 특히 재즈의 "II-V-I" 진행에서 많이 사용된다. 예를 들어 C key에서 Dm7-G7-CM7이 2-5-1 진행이 되는데, G7의 대리코드로 Db7을 사용하면 Dm7-Db7-CM7이 되어 자연스럽게 chromatic root movement가 생기게 된다.
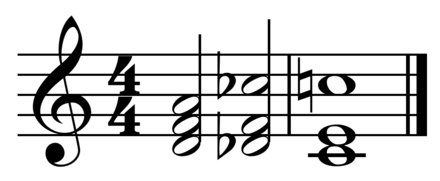
5) Tonic substitution
· 주로 tonic chord (I chord)의 대리코드로 iii과 vi가 많이 쓰인다. 예를 들어 C major key라고 하면 CM7 (C, E, G, B)은 iii chord인 Em7 (E, G, B, D) 및 vi chord인 Am7 (A, C, E, G)으로 대리될 수 있다.
· tonic chord의 대리코드인 iii, vi chord는 원래는 tonic chord를 위해 디자인된 멜로디를 뒷받침하는 역할을 하게 된다. 예를 들어 Em7은 CM9에서 루트를 생략한 코드이고, Am7은 C6에서 6도음인 A를 루트로 자리바꿈한 코드라고 생각할 수 있다.[2]
6) Relative major/minor substitution
· C major와 A minor 간의 관계와 같은 것이다.
7) augmented triad
· V+를 substitute dominant로 사용할 수 있다. 또한 bIII+를 substitute dominant로 사용가능하다. 예를 들어 C key에서 원래는 G7이 와야 할 자리에 G+ (G, B, D#)를 사용하거나 Eb+ (Eb, G, B)를 사용할 수 있다. (G, B를 공유한다)

8) bVII7
· 이 코드 또한 dominant의 대리 코드로 사용될 수 있는데 이는 종종 IV7이 선행하여 backdoor progression을 이루게 된다. 예를 들어 C key에서 G7 (G, B, D, F)가 Bb7(Bb, D, F, Ab)으로 대리될 수 있고, 이 앞에 IV7이 선행할 수 있다.

여기까지의 내용은 위키의 내용을 정리한 것인데, 크게 보면 대부분 dominant의 대리 코드로 무엇을 쓸 수 있는지에 대한 설명이 많았고, tonic의 대리 코드에 관한 내용도 약간 있었다.
3. 응용
1) Tonic의 대리코드로 #IV(b5)m7를 사용할 수 있다.[2]
FM7의 A, C, E는 두 tonic인 Am7과 C6의 중심 조합으로써 매우 훌륭한 조합이다. 그러나 FM7의 경우 subdominant로써의 성격이 지나치게 강하므로, 좀 더 흐름이 좋도록 1음만 #하여 F#(b5)m7을 만든다. 이러한 대리코드는 곡의 중간에 사용하는 것이 좋다. 예를 들어 dominant-tonic-subdominant의 진행이 있다고 하면 G7-CM7-FM7의 진행이 전형적이다. CM7 대신에 대리코드인 F#(b5)m7을 사용하면 베이스 라인이 G-F#-F가 되어 다소 부드럽게 진행하게 된다.
[1] Wikipedia. Chord substitution. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chord_substitution.
[2] http://www.nazuni.pe.kr/art/theory/harmonics/substitute_chord.php
'음악 > 레슨, 강의, 유튜브 정리' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Extended chord를 이용해 연주하기 (0) | 2019.11.01 |
|---|---|
| Altered Scale (얼터드 스케일), 도대체 넌 뭐니? (0) | 2019.10.30 |
| Diatonic seventh chords의 reharmonization (0) | 2019.09.16 |
| 워킹 베이스란? 워킹 베이스는 어떻게 칠까? (1) | 2019.07.17 |




